Introduction
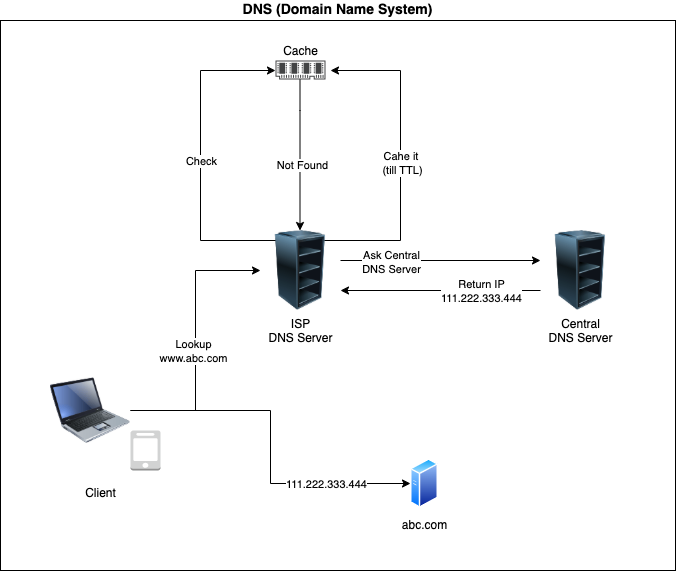
DNS (Domain Name System) which translates domain names like www.abc.com to IP address.
Architecture
Caching takes place at ISP as well as browser end once the IP is received from central DNS server. TTL (Time to Live) configuration determines till what time the DNS record can be cached after that it must be fetched again.
There are different types of DNS records,
- NS Record : Specifies the DNS server for domain/subdomain.
- MX Record: Specifies the mail server for accepting the messages.
- A Record: Points name to IP.
- CNAME: Points name to another canonical name.
DNS Services can also be used for balancing the load by routing the traffic. Different methods are there for balancing the load through DNS,
- Round Robin (Weighted Round Robin preferably)
- Latency Based
- Geolocation Based
For example, DNS can return IP of US instead of Africa for www.abc.com to the user located in US.
DDoS Attack
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is a cyberattack that disrupts a network service, such as a website or server. The goal of a DDoS attack is to make the target inaccessible by overwhelming it with traffic.